The Quantumplators for QCHack 2021
Salute readers !
We , the 'Quantumplators' are a group of Quantum fanatics who took part in the QCHack 2021.
This blog is an abecedarian approach to communicate to our readers the basics of our Free form
project and what motivated us to choose the problem statement.
The realm of Quantum Computing is a field of invigorating possibilities. Though the field has been active since the 70’s , the technical strides are quite recent.
In this challenge, we attempted to leverage the Grover’s Algorithm in solving a simple problem, which
could have had a higher complexity had it been performed on a classical computer.
The key idea we made use of like any other Quantum Algorithm was to leverage the property of
‘Superposition of states’ . The very fact that the qubit can exist in a superposition of states is both
intriguing and very useful. For certain ranges of computation, it helps make a more efficient code
and reduce the running time complexity.
Our algorithm aims to find the least value of the qubit in an array without having to sort the array.
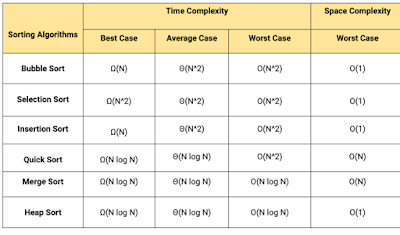
The conventional search algorithms generally require the linked list or the array to be sorted (for
example by using Bubble Sort, Quicksort, etc.) thus increasing the running time, complexity and
reducing the efficiency of the algorithm.
We are applying the Grover’s search algorithm and an oracle to help search an item in an array.
We propose our approach is more powerful than the classical approach because here , we need not sort our array to locate an element.
The advantages of this approach are the reduced complexity and enhanced computation speed.
This is owing to the use of the Grover's search algorithm enhanced efficiency.
The Strategy:
The oracle has been developed for two numbers due to constraints on time. The oracle takes in two numbers and highlights the bits of the smaller number by flipping its phase. This then goes through the Grover diffusion matrix where the highlighted bits are amplified. Thus, when the system is measured, the smaller number is highlighted.
In its current state, multiple numbers can be compared using cascaded approach. However, the computational prowess of Microsoft Teams can be used to calculate multiple numbers at the same time - one approach being the exploitation of quantum parallelism.
Have a happy quantum cruise !
- Team Quantumplators
Mahnoor Fatima, Salma El amraoui, Majd Safi, Rita Abani and Adam Gluck











Comments
Post a Comment